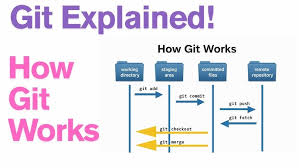
Components of the Diagram
1. Remote Repo: A central repository where changes are pushed and fetched from.
2. Local Sections: Two identical sections representing the workflow of two developers. Each includes:
– Developer: Represented by an icon of a person working on a laptop.
– Working Directory: Where files are edited.
– Staging Area: Where changes are staged using `git add`.
– Local Repo: Where changes are committed using `git commit`.
Git Operations
The diagram shows the following Git operations:
– edit: Developer edits files in the Working Directory.
– git add: Moves changes to the Staging Area.
– git commit: Commits changes to the Local Repo.
– git push: Pushes changes from Local Repo to Remote Repo.
– git fetch: Fetches changes from Remote Repo to Local Repo.
– git checkout: Switches between different states or branches (implied in the workflow).
Workflow
The workflow for each developer is:
1. Edit files in the Working Directory.
2. Stage changes using `git add`.
3. Commit changes using `git commit`.
4. Push changes to the Remote Repo using `git push`.
5. Fetch changes from the Remote Repo using `git fetch`.
The diagram effectively illustrates the basic Git workflow and interaction between local and remote repositories for multiple developers.