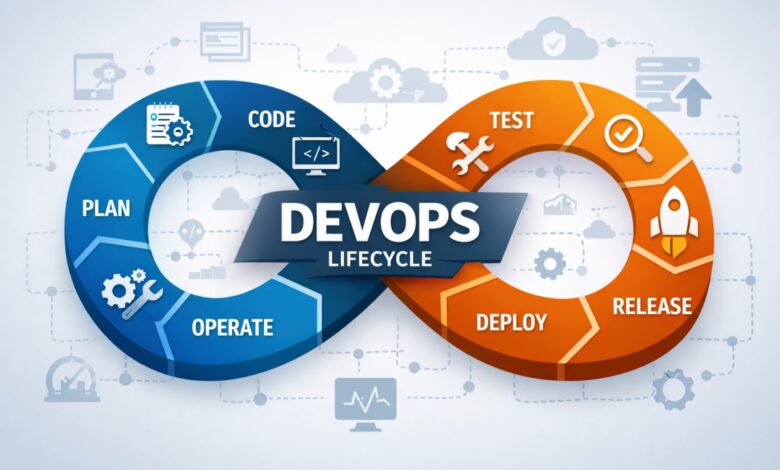
DevOps is not a single tool or technology—it is a culture and practice that brings development and operations teams together to deliver software faster, more reliably, and at scale.
At the heart of DevOps lies the DevOps toolchain: a set of integrated tools that support every stage of the software delivery lifecycle.
This article explains the DevOps toolchain end-to-end, covering tools used for planning, building, testing, deploying, monitoring, and configuration in simple and practical terms.
What Is a DevOps Toolchain?
A DevOps toolchain is a collection of tools that automate and integrate processes across the DevOps lifecycle.
Each tool focuses on a specific phase, but when combined, they create a continuous workflow known as CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery).
Key goals of a DevOps toolchain:
-
Faster software delivery
-
Reduced manual errors
-
Better collaboration
-
Continuous feedback and improvement
-
High system reliability in production
1. Planning Tools
Planning tools help teams define requirements, track progress, and manage tasks.
Purpose:
-
Requirement gathering
-
Sprint planning
-
Issue and bug tracking
-
Collaboration between teams
Popular tools:
-
Jira
-
Azure Boards
-
Trello
Why they matter:
Good planning ensures clarity, accountability, and alignment between business and engineering teams.
2. Source Code Management (SCM)
SCM tools manage application source code, track changes, and enable collaboration.
Purpose:
-
Version control
-
Branching and merging
-
Code history and rollback
-
Team collaboration
Popular tools:
-
Git
-
GitHub
-
GitLab
-
Bitbucket
Why they matter:
SCM is the foundation of DevOps—everything starts with code.
3. Build Tools
Build tools convert source code into executable artifacts.
Purpose:
-
Compile code
-
Resolve dependencies
-
Generate build artifacts (JAR, WAR, binaries)
Popular tools:
-
Maven
-
Gradle
-
npm
Why they matter:
Automated builds reduce human errors and ensure consistent outputs across environments.
4. Testing Tools
Testing tools validate application quality through automated testing.
Purpose:
-
Unit testing
-
Integration testing
-
Performance and load testing
-
Security testing
Popular tools:
-
Selenium
-
JUnit
-
TestNG
-
JMeter
Why they matter:
Early and automated testing helps catch bugs before production, saving time and cost.
5. Continuous Integration & Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
CI/CD tools automate the build, test, and deployment pipeline.
Purpose:
-
Automatic code integration
-
Pipeline automation
-
Faster releases
-
Reduced deployment risk
Popular tools:
-
Jenkins
-
GitHub Actions
-
GitLab CI/CD
-
Azure DevOps
Why they matter:
CI/CD enables frequent, reliable, and automated deployments.
6. Deployment & Containerization Tools
These tools help package applications and deploy them consistently.
Purpose:
-
Container creation
-
Application isolation
-
Environment consistency
-
Scalable deployments
Popular tools:
-
Docker
-
Kubernetes
-
Amazon ECS
-
Helm
Why they matter:
Containers solve the classic problem: “It works on my machine.”
7. Configuration Management & Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
These tools manage infrastructure using code and automation.
Purpose:
-
Server provisioning
-
Configuration consistency
-
Infrastructure versioning
-
Automated scaling
Popular tools:
-
Ansible
-
Terraform
-
Chef
-
Puppet
Why they matter:
IaC makes infrastructure repeatable, auditable, and scalable.
8. Monitoring, Logging & Observability
Monitoring tools provide visibility into system health and performance.
Purpose:
-
Detect failures
-
Track performance metrics
-
Analyze logs
-
Improve reliability
Popular tools:
-
Prometheus
-
Grafana
-
ELK Stack
-
AWS CloudWatch
Why they matter:
Monitoring answers “Is something wrong right now?”, while observability explains “Why did it happen?”
How All Tools Work Together
The real power of DevOps comes from integration:
-
Planning tools → define work
-
SCM → manage code
-
Build & test → ensure quality
-
CI/CD → automate delivery
-
Containers & IaC → ensure consistency
-
Monitoring → provide feedback
This creates a continuous feedback loop for improvement.